1. Which of the following statements best describes the structure and purpose of a bundled payment model in spine care?
Correct Answer: It links payment for related services during a care episode to a target cost, promoting standardization and efficiency
Explanation:
Bundled payment models assign a single payment for all services delivered during an episode of care. The goal is to improve value by reducing variability, limiting low-value interventions, and encouraging efficiency in clinical decision-making. Unlike fee-for-service, bundled models reward providers for quality and coordinated care, not volume.
Click here for further reading.
2. Which factor does NOT correlate with subjective well-being in SCI patients?
Correct Answer: Level of injury
Explanation:
The level of injury does not correlate with subjective well-being in spinal cord injury (SCI) patients. While one might assume that the severity or location of the injury would directly impact a patient's well-being, research indicates that factors such as the completeness of the injury, social support systems, and marital status have more significant correlations with how patients perceive their quality of life. These elements can influence emotional and psychological adaptation, which plays a crucial role in subjective well-being. For more detailed information, please see the Knowledge Now article "SCI Traumatic Part One: Disease/Disorder and Essentials of Assessment."
Click here for further reading.
3. Which region of the spine is most commonly affected by radiculopathies?
Correct Answer: Lumbosacral spine (L5-S1)
Explanation:
Radiculopathies predominantly affect the lumbosacral nerve roots, accounting for approximately 60% to 90% of all cases, with the majority involving the L5 and S1 roots. In contrast, cervical radiculopathies constitute about 5% to 10% of cases, primarily impacting the C7 and C6 roots, while thoracic radiculopathies are rare, representing only 0.15% to 4% of symptomatic disc herniations.
Click here for further reading.
4. What is the most common cause of traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) in the general population?
Correct Answer: Motor vehicle accidents
Explanation:
The most common cause of traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) in the general population is motor vehicle accidents. These incidents typically result in high-impact trauma, which can lead to significant damage to the spinal cord, resulting in varying degrees of motor, sensory, and autonomic dysfunction. Motor vehicle accidents have consistently been the leading cause of SCI, highlighting the importance of road safety and preventive measures. For more detailed information, please see the Knowledge Now article "SCI Traumatic Part One: Disease/Disorder and Essentials of Assessment."
Click here for further reading.
5. What is the primary determinant of overall function after SCI?
Correct Answer: Motor function
Explanation:
The primary determinant of overall function after a spinal cord injury (SCI) is motor function. This refers to the ability of the individual to perform movements and tasks, which directly impacts their level of independence and quality of life. Motor function recovery is a critical factor in rehabilitation and can significantly influence the prognosis and long-term outcomes for patients with SCI. For more detailed information, please see the Knowledge Now article "SCI Traumatic Part One: Disease/Disorder and Essentials of Assessment."
Click here for further reading.
6. Which medication acts as a GABA B agonist and is used to manage spasticity?
Correct Answer: Baclofen
Explanation:
Baclofen acts as a GABA B agonist, reducing muscle tone in spasticity management. Option A, Diazepam, is a GABA A agonist. Option B, Tizanidine, is an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist. Option D, Gabapentin, inhibits voltage-gated calcium channels, none of which correspond to GABA B agonism.
Click here for further reading.
7. Which of the following is a positive feature of the upper motor neuron syndrome associated with spasticity?
Correct Answer: Clonus
Explanation:
Clonus, characterized by repetitive, rhythmic muscle contractions, is a positive feature of the upper motor neuron syndrome. Option A, muscle weakness, is a negative feature, indicative of loss of function. Option B, loss of dexterity, also represents a negative feature as it reflects decreased motor skills. Option C, easy fatigability, is a negative feature, indicating a decline in performance over time.
Click here for further reading.
8. What is the primary role of a physiatrist in a stroke rehabilitation care pathway according to the AAPM&R Stroke Rehabilitation Toolkit?
Correct answer: To oversee the care transitions and coordinate interdisciplinary treatment across the continuum
Explanation:
The physiatrist plays a critical leadership role in managing stroke rehabilitation. According to the toolkit, this includes evaluating patients at different stages of recovery, coordinating transitions between care settings (e.g., IRF, SNF, home care), and leading interdisciplinary teams to optimize medical and functional outcomes. They do not perform surgery, and while they may interact with insurance and outpatient care, their broader role centers on continuity and coordination of comprehensive rehabilitative care.
Click here for further reading.
9. Which condition, often diagnosed through CT scanning as the first-line imaging modality, involves bleeding into the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering it, frequently caused by a ruptured aneurysm?
Correct Answer: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Explanation:
A Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH), a serious medical condition characterized by bleeding into the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering it. According to the article, CT scanning is the first-line imaging technique for detecting brain hemorrhages, including SAH, due to its speed and high sensitivity in identifying acute bleeding. MRI may also be used in some cases for further evaluation. SAH is most commonly caused by a ruptured aneurysm, making prompt diagnosis crucial for effective treatment and management. Incorrect answers like Epidural Hematoma, Ischemic Stroke, and Brain Tumor involve different underlying mechanisms and imaging findings, highlighting the importance of proper imaging techniques for accurate diagnosis.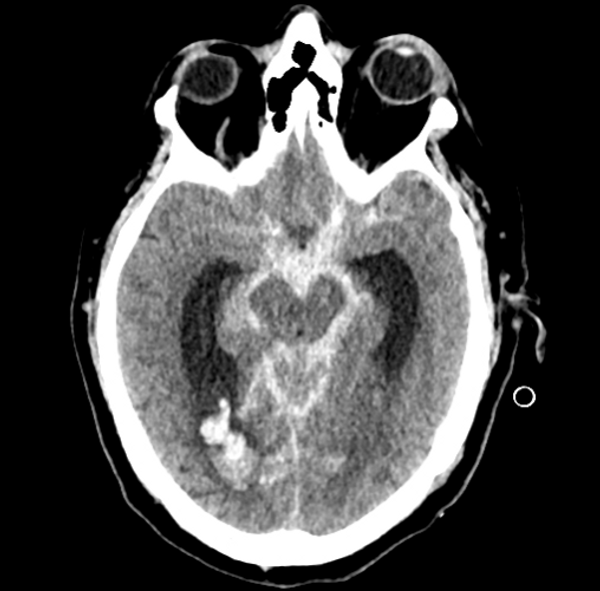
Click here for further reading.
10. Identify the anomalous innervations on this EMG.
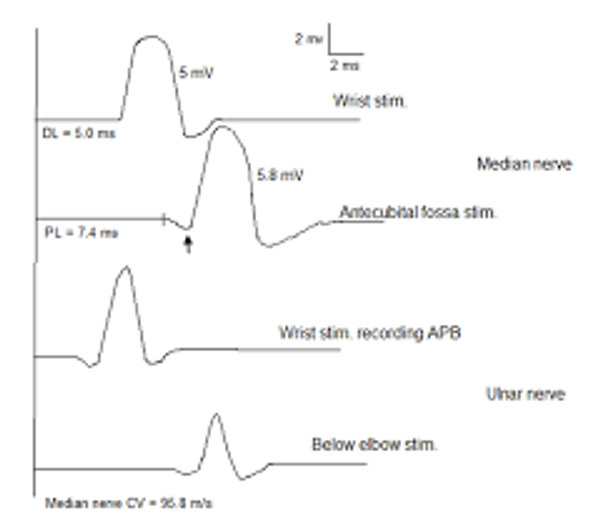
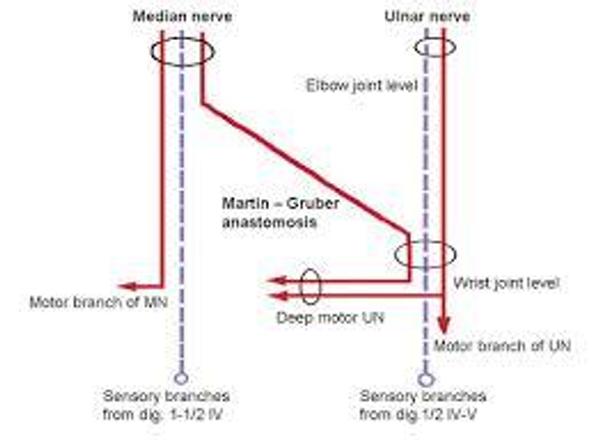
Correct Answer: Martin Gruber Anastomosis
Explanation:
A proximal positive dip in the motor median nerve conduction study is indicative, specially in the presence of CTS, is indicative of Martin Gruber Anastomosis.
Click here for additional reading.