1. What is the common presentation of popliteal artery entrapment?
Correct Answer: cramping in calf with exercise, disappears with rest
Explanation:
PAES occurs when the popliteal artery, which runs behind the knee, is compressed by muscles or tendons in the popliteal fossa (the area behind the knee).
Causes: Anomalous anatomy: An abnormal relationship between the artery and surrounding muscles or tendons can lead to compression.
Muscle hypertrophy: Enlarged calf muscles, especially in athletes, can put pressure on the artery.
Symptoms: Exercise-related pain: Pain, numbness, or cramping in the calf or foot during exercise, often relieved by rest. Claudication: Pain in the calf or foot that occurs with walking or exercise and is relieved by rest. Swelling: Swelling in the calf area.
Changes in skin color: Changes in skin color around the calf muscle.
Click here for further reading.
2. Which hip structure results in a "sports hernia"
Correct Answer: rupture of adductor magnus
Explanation:
Transversalis fascia tear results in hernia.
For additional reading, click here.
3. Which of the 5 flexor (volar) zones are referred to as worse for injuries?
Correct Answer: Zone 2
Explanation:
A flexor or finger pulley is the name given for the annular connective tissue that keeps the finger tendons close to the bone. Dynamic ultrasound assists in diagnosis. Zone 2 injuries are the worst due to risk of adhesions.
For additional reading, click here.
4. What is role of Baxter's nerve?
Correct Answer: entrapment
Explanation:
May be confused with plantar fasciopathy
For additional reading, click here.
5. What is this lesion called on the x-ray views of the knee?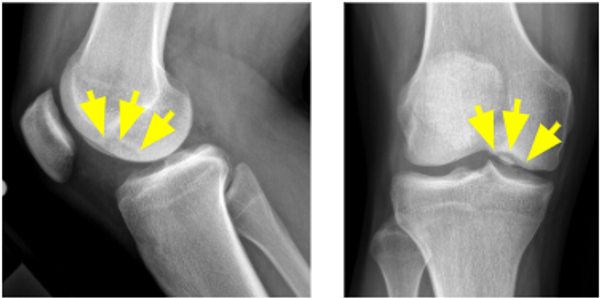
Correct Answer: Osteochondritis dissecans
Explanation:
This image shows an tunnel/notch and lateral x-ray views of the knee that demonstrate an osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) lesion of the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle.
OCD is a condition that develops in joints in children and adolescents. It occurs when a small segment of bone begins to separate from its surrounding region due to a lack of blood supply. As a result, the small piece of bone and the cartilage covering it begin to crack and loosen.
The most common joints affected by osteochondritis dissecans are the knee, ankle and elbow, although it can also occur in other joints. The condition typically affects just one joint; however, some children can develop OCD in several joints.
In many cases of OCD in children, the affected bone and cartilage heal on their own, especially if a child is still growing.
In grown children and young adults, OCD can have more severe effects. The OCD lesions have a greater chance of separating from the surrounding bone and cartilage and can even detach and float around inside the joint. In these cases, surgery may be necessary.
Click here for further reading.
6. What is this finding on x-ray?
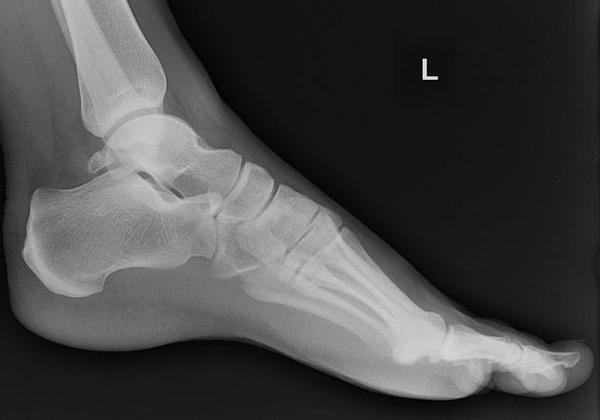
Correct Answer: Os trigonum
Explanation:
The os trigonum is a small, accessory bone located at the back of the talus (a bone in the ankle). It forms when a secondary ossification center in the talus fails to fuse during development. While often asymptomatic, it can sometimes cause pain and impingement in the ankle, especially in athletes or dancers, a condition known as os trigonum syndrome. This is also called "nutcracker phenomenon"
For additional reading, click here.
7. What is the anatomical finding in this knee xray?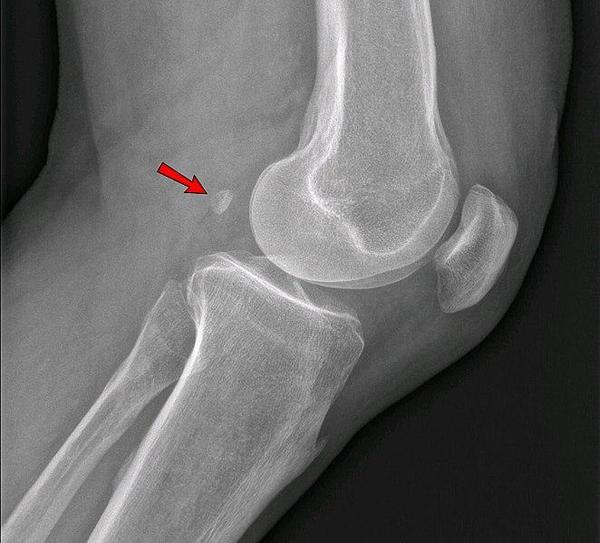
Correct Answer: fabella
Explanation:
This finding is a fabella which is a normal finding on xray and is a sesamoid bone embedded in a tendon on the posterior aspect of the knee.
8. An otherwise healthy 50-year-old female presents with persistent axial low back pain after a fall 4 months ago. What "can't miss diagnosis" should you consider?
Correct Answer: vertebral compression fracture
Explanation:
Vertebral compression fracture is usually caused by a low velocity fall in patients with osteoporosis. Patients can develop osteoporosis starting in the 5th decade and should be added to your differential diagnosis. Persistent, severe axial low back pain could be caused by the other diagnoses, but you would not want to miss a fracture.
For further reading, click here.
9. What abnormal spinal finding does this X-ray finding demonstrate?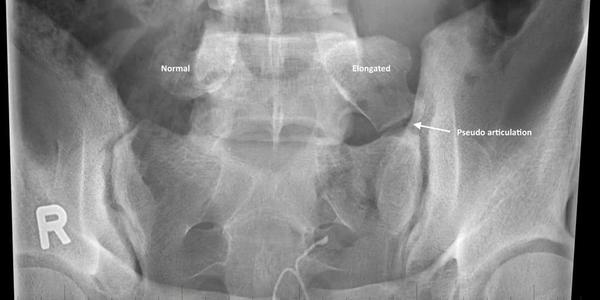
Correct Answer: Bertolotti’s
Explanation:
Bertolotti's is a joint formed between the L5 TP and the sacrum, which can serve as a pain generator.
10. An otherwise healthy 50-year-old female presents with persistent axial low back pain after a fall 4 months ago. MRI lumbar spine is shown. What is your next best step in management?
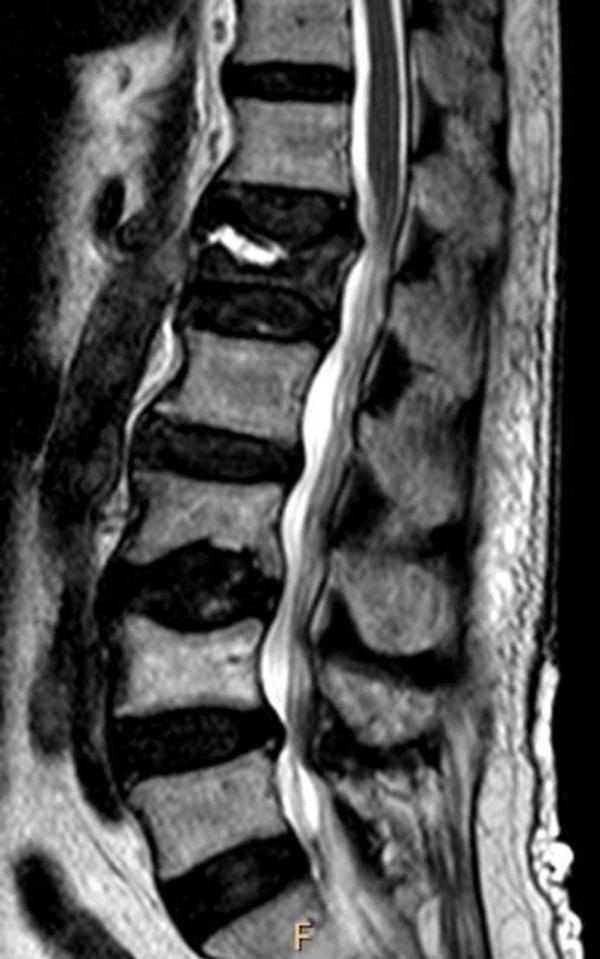
Correct answer: DEXA scan
Explanation:
This patient has a vertebral compression fracture in the lumbar spine. The next best step would be to diagnosis osteoporosis with a DEXA scan. CT scan would not add any additional information at this time. Vitamin D level might be low but would not help you diagnose osteoporosis.